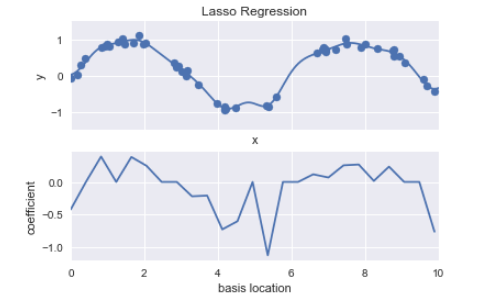
昨天介紹完Linear Regression,今天要來繼續介紹高斯函數在Linear-Regression的應用。高斯函數本身不是SKlearn中的模組,因此,需要自己編寫一個自訂的高斯函式:
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
class GaussianFeatures(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):
"""Uniformly spaced Gaussian features for one-dimensional input"""
def __init__(self, N, width_factor=1.0):
self.N = N
self.width_factor = width_factor
@staticmethod
def _gauss_basis(x, y, width, axis=None):
arg = (x - y) / width
return np.exp(-0.5 * np.sum(arg ** 2, axis))
def fit(self, X, y=None):
# create N centers spread along the data range
self.centers_ = np.linspace(X.min(), X.max(), self.N)
self.width_ = self.width_factor * (self.centers_[1] - self.centers_[0])
return self
def transform(self, X):
return self._gauss_basis(X[:, :, np.newaxis], self.centers_,
self.width_, axis=1)
gauss_model = make_pipeline(GaussianFeatures(20),
LinearRegression())
gauss_model.fit(x[:, np.newaxis], y)
yfit = gauss_model.predict(xfit[:, np.newaxis])
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(xfit, yfit)
plt.xlim(0, 10);
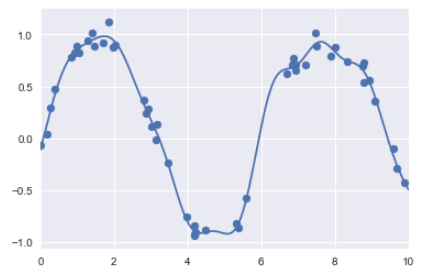
model = make_pipeline(GaussianFeatures(25), Lasso(alpha=0.001))
basis_plot(model, title='Lasso Regression')